Fertilizing
|
Fertilizing will vary from plant to plant (flowering and deciduous plants have different requirements than junipers or other evergreens), so it is highly recommended that you do background research on your specific plant in order to ensure proper care.
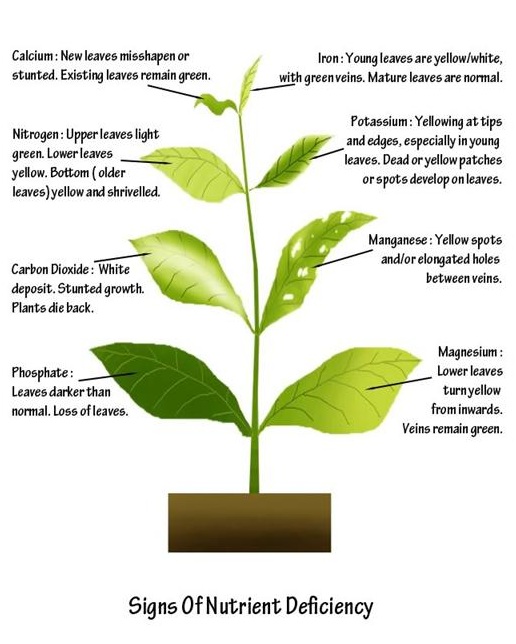
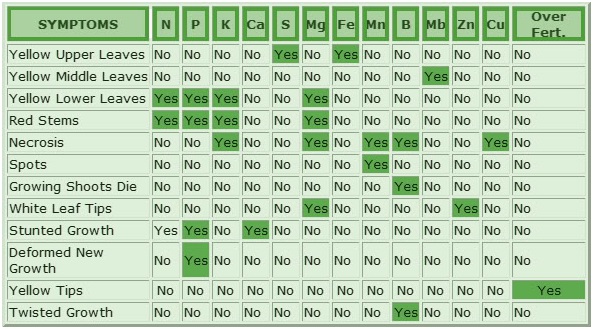
Generally speaking though, a water-soluble fertilizer is usually applied every 2 to 4 weeks during the growing season, in a half-strength solution. The most common types of fertilizer contain NPK, nitrogen (N), phosphates (P) and potassium (K). Beyond these three, bonsai need a number of other nutrients, including iron (Fe), potash, and vitamins (especially B-vitamins). Miracle-Gro or Miracid are commonly used, but check label directions for your tree. Do not feed right after repotting (wait for 3-4 weeks). Don't feed if the tree is sickly. Make sure to moisten the plant soil first (never feed a very dry bonsai). If you plan on fertilizing during the fall or winter, use a 0-10-10 fertilizer (lacks nitrogen), but contains phosphorus and potassium for trunk, root and for future spring growth. For a general purpose fertilizer, the Green Dream Organic Bonsai Fertilizer located on the right, is one of the best fertilizers out there. It is a 7:5:5 fertilizer and produces amazing results, even though it's quite smelly. If you go with it, you won't be disappointed, but it is recommended that you use it for outdoor trees to avoid having to smell it. Here is a basic run-through of N-P-K and their effects: Nitrogen (N) - Promotes growth of leaves. Excess nitrogen diminishes the immune system of the tree and excessive nitrogen will cause the leaves to be undeveloped and yellow. Phosphorus (P) - Promotes growth of roots and flowers. Trees do not uptake excessive phosphorus, so the only danger is a lack of it, which is characterized by reddish hued leaves. Potassium (K) - Promotes the growth of wood, flowers and fruit. A lack of potassium results in brown spots on the leaves. |
|